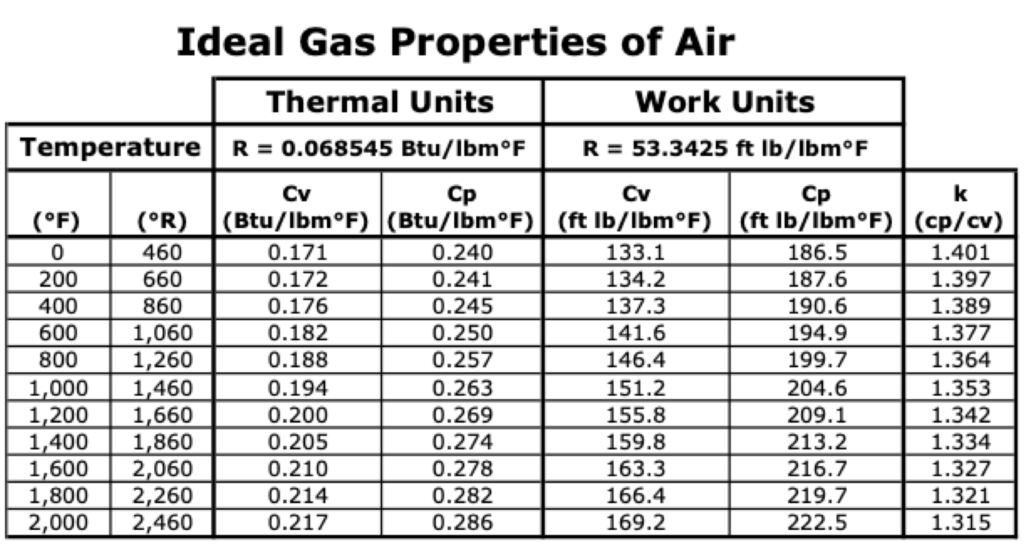
Air is a mixture of gases. By volume, air is 78.084% Nitrogen, 20.946% Oxygen, 0.934 % Argon, and just traces of CO2, neon, methane, helium and others. The molecular weight of the combined molecules is MAIR = 28.97. Water vapor is important and exists at varying levels depending on weather conditions. For the purposes of engine tuning the oxygen is usually rounded to about 21%, and all the others are lumped together to make 79% nitrogen.
Standard Air
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is an agreed upon baseline for air. ISA conditions at sea level are 59°F, 14.69 psia with no water vapor. The air density is 0.0765 lbm/ft3 at standard conditions, so a pound of air occupies 1 / 0.0765 lbm/ft = 13.08 ft3/lbm. That’s a box just over 28.25 inches per side.
Air Density Ratio
Weather stations can give an air density ratio (ADR). It is the actual density relative to the ISA density. The actual outside air density and volume as determined by a weather station is:
Air Density = ADR * 0.0765 lbm/ft3
and
Air Volume per pound = 13.08 ft3/lbm / ADR
Air Ideal Gas Constant
The Ideal Gas Law (PV = mRT) can be used to estimate the properties of air at changing conditions. For example, the volume of 1 lbm of air at standard conditions would be:
m = 1 lbm
RAIR = RU / MAIR = 1,545.349 / 28.97 = 53.34 ft-lb/lbm°F
T = 59 °F + 459.67 = 518.67 °R (Converts temperature °F to absolute °R)
P = 14.69 psi * 144 in2/ft2 = 2,115.36 lb/ft2 (Converts psi to lb/ft2)
V = mRT/P = 1 * 53.34 * 518.67 / 2115.36 = 13.08 ft3
Density = m/V = ρ = P/RT = P / (53.34*T) = 2,115.36 / (53.34 * 518.67) = 0.0765 lbm/ft3
Specific Heat
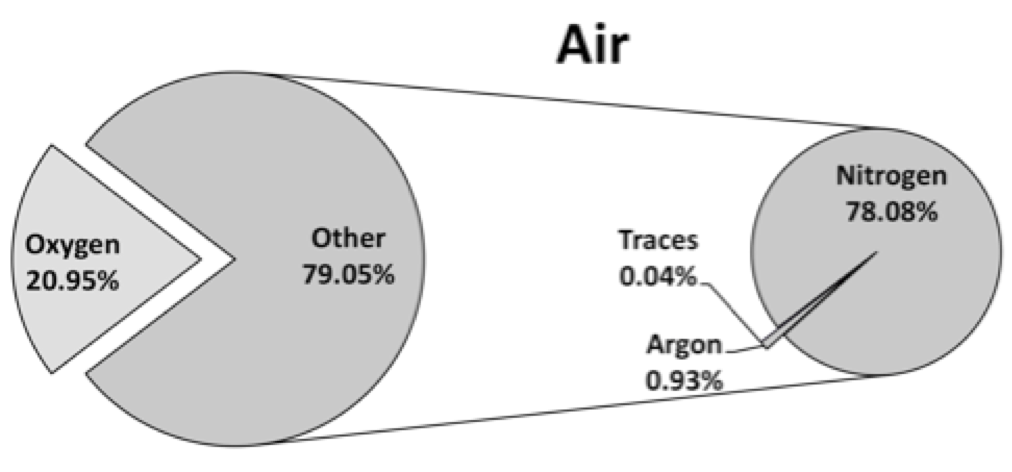
The specific heat is the amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of a substance. Liquid water’s specific heat of 1.0 Btu/lbm °F is the highest known and is the reference for all others. The specific heat of gas is determined by heating while maintaining constant pressure (cPAIR = 0.24 Btu/lbm °F) or constant volume (cVAIR =0.171 Btu/lbm °F). The specific heat ratio, kAIR = cPAIR / cVAIR = 0.24 / 0.171 = 1.4, is often used in engine analysis. The specific heat varies some with temperature. At the high temperature in engines the error can become fairly large if the properties are held constant. Tables of the properties over the entire useful temperature range are available from NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology).
Air Properties
Molecular Weight MAIR = 28.97
Gas Constant RAIR = RU / MAIR = 1,545.349 / 28.97 = 53.34 ft-lb/lbm°F